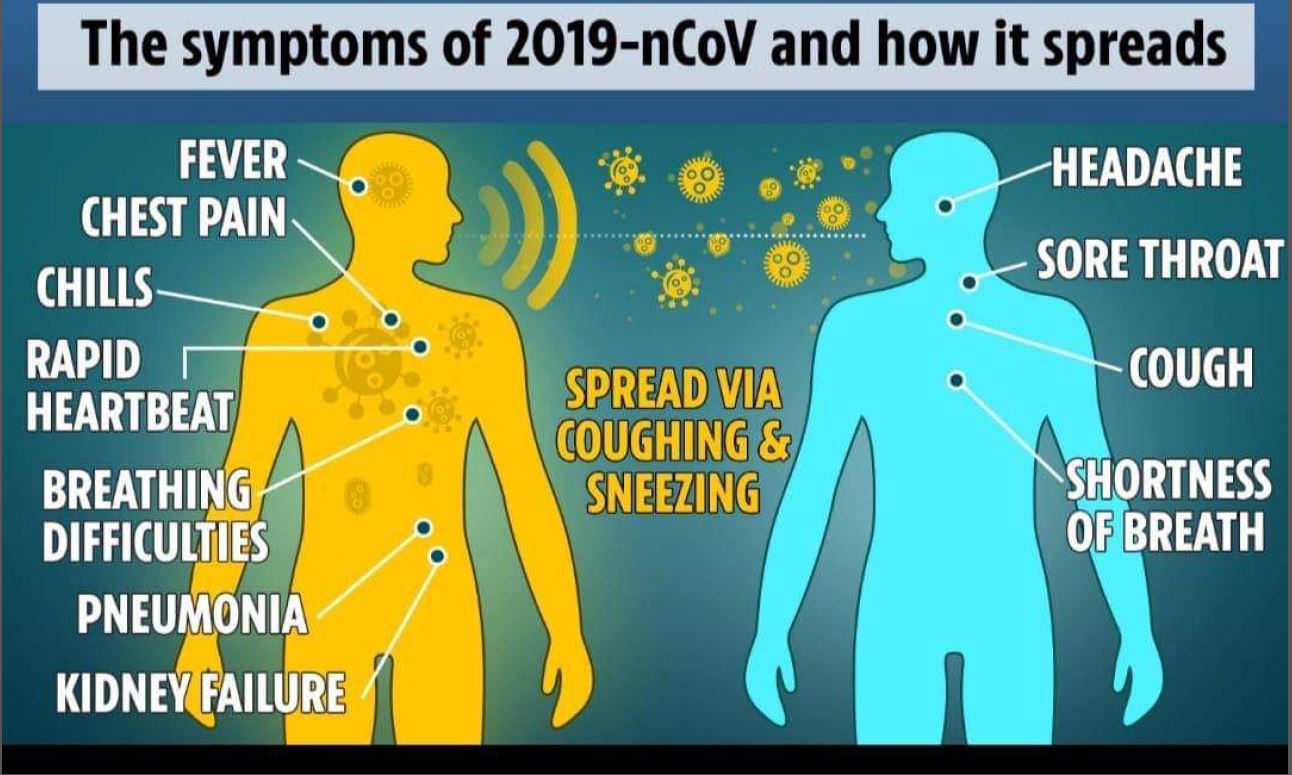
An outbreak of 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing severe acute respiratory illness has been reported in Wuhan, China since December 21, 2019. The virus has not been previously identified so little is known about it, including its origin. Initial cases identified, however, have been linked to Wuhan South China Seafood City (also called the South China Seafood Wholesales Market and the Hua Nan Seafood Market), where, in addition to seafood, chickens, bats, cats, marmots, and other wild animals are sold, suggesting a possible zoonotic origin to the outbreak (CDC). Confirmed cases of novel coronavirus have now been documented in other countries, with most infected persons having recently traveled to China and a few cases of person-to-person transmission being observed.
What is a coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are known to cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV).
What is a novel coronavirus?
A novel coronavirus (CoV) is a new strain of coronavirus that has not been previously identified in humans.